Jane ChambersBusiness reporter, Asunción, Paraguay
 Gabriela Cibils
Gabriela CibilsGabriela Cibils is on a mission – to help turn Paraguay into the Silicon Valley of South America.
When she was growing up in the landlocked country, nestled between Brazil and Argentina, she says the nation “wasn’t super tech focused”.
But it was different for Ms Cibils, as her parents worked in the technology sector. And she was inspired to study in the US, where she got a degree in computing and neuroscience from the University of California, Berkeley.
After graduating she spent eight years working in Silicon Valley, near San Francisco, with roles at various American start-ups.
But rather than staying permanently in the US, a few years ago she decided to return home to Paraguay. She’s now helping to lead efforts to build a large and successful tech sector that puts the country of seven million people on the world map – and attract some of the globe’s tech giants.
 AFP via Getty Images
AFP via Getty Images“I saw first hand the impact that technology can have on your life,” says Ms Cibils. “After being exposed to such a different world [in Silicon Valley], it’s my responsibility to bring that mindset back and combine it with the talent I see in Paraguay.”
She is now a partner at global technology and investment firm Cibersons, whose headquarters is in Paraguay’s capital Asunción.
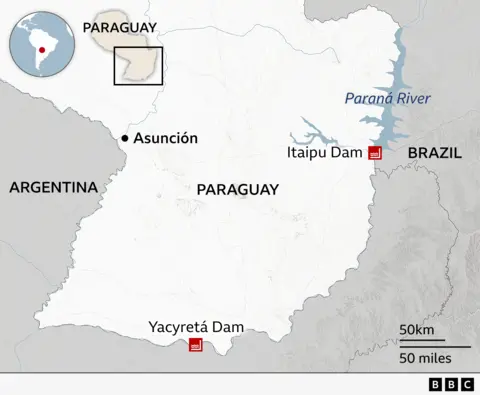
While most countries would love to build a world-class tech sector, Paraguay has a distinct advantage in one regard – an abundance of cheap, green electricity.
This is thanks to 100% of its generation now coming from hydroelectric power.
This is centred on the giant Itaipu Dam on the Paraná River, which forms part of the border between Paraguay and Brazil. This huge hydroelectric power station, the largest in the world outside of China, supplies 90% of Paraguay’s electricity needs, and 10% of Brazil’s.
In fact, such is Paraguay’s surplus of electricity that its electricity prices are the lowest in South America.
And it is the world’s largest exporter of clean energy.
The Paraguayan government hopes that the country’s abundance of cheap, green electricity will attract global tech firms increasingly focused on the massive energy demands of AI computing.
“If you want to install any technology investment like AI data centres, keep in mind hydroelectric power is both renewable and steady,” says Paraguayan software development entrepreneur Sebastian Ortiz-Chamorro.
“Compared to other renewable energy sources like wind or solar, that have their ups and downs, it’s much more attractive for creating data centres or any other electro intensive activity that requires a steady electricity source.”
He adds that in addition to Itaipu, and Paraguay’s other large state-owned hydroelectric plant, the Yacyretá Dam, private companies can easily build their own smaller facilities.
On a visit to California last year Paraguay’s President Santiago Peña spoke with companies like Google and OpenAI to encourage them to invest in Paraguay. It remains to be seen if such industry giants open large operations in the country.
Minister of Technology and Communication Gustavo Villate is working closely with the president on the continuing efforts.
“We have the youngest population. We have a lot of renewable green energy. We have low taxes and economic stability,” he says proudly.
I’m taken on a tour with the minister of a planned new digital park near Asunción’s main airport. It’s currently green fields and some army barracks.
Mr Villate unfurls plans to show off the lakes, a childcare centre and other buildings which he says should be ready in under two years.
“The government are going to invest around $20m (£15m) for the first stage, but the idea is for private companies to invest the rest,” he says.
Even though the park isn’t ready yet, Mr Villate says the collaboration already happening between the public, private and university sectors is key to building an ecosystem to attract foreign investors.
The government thinks the country’s young population will be a key attraction, and able to provide a large tech workforce. The average age in Paraguay is 27.
 Vanessa Cañete
Vanessa CañeteBut more young people will need to be trained. The technology minister says the new digital park will also be home to The University of Technology, which is a joint venture between Taiwan and Paraguay.
Meanwhile, there are other initiatives to train young people in the country. “We are working really hard to create a mass of software engineers, programmers and everything you need to provide software services,” says Vanessa Cañete, president of trade group Paraguayan Chamber of the Software Industry.
Ms Cañete says she is also passionate about encouraging more women to study computer engineering. In 2017 she set up Girls Code, a non-profit association which aims to close the tech gender gap.
It organises programming and robotics workshops for teenagers and young women, with more than 1,000 receiving some sort of training to date.
Ms Cañete adds that software developers are also given English lessons for up to four years to improve their communication with overseas firms.
The people I met are brimming with positivity about what Paraguay has to offer the tech world, but they are also pragmatic.
Ms Cibils says there are still “growing pains” for foreign investors, with issues like bureaucracy, which can hold things up adapting local contracts to standardised international ones.
But she is adamant that “if you put innovation at its core and leverage all the benefits that the country has I think Paraguay can be a superpower”.



