Colorectal cancer (CRC), once mainly a disease attacking older adults, is being diagnosed more and more in younger people as well. Many health experts have sounded alarm on its early-onset cases, because often diagnosis is delayed and the disease tends to be more aggressive. Understanding why it is increasing day by day, and spotting what to watch out for, can make a major difference.As per, WHO by 2040 the burden of colorectal cancer will increase to 3.2 million new cases per year (an increase of 63%) and 1.6 million deaths per year (an increase of 73%).What aggravates this rise even further is that the majority of such cases are diagnosed at advanced stages of the disease, mainly because, all the early symptoms can be even more subtle or mistaken for milder diseases. By the time patients seek medical help, the cancer may have already reached advanced stages, thereby treatments are even more challenging. It is important to understand the causes behind such a radical shift, and not just for those on the at-risk list but for healthcare practitioners and the population as a whole.
Why is colorectal cancer rising among younger adults:
Dietary and lifestyle factors
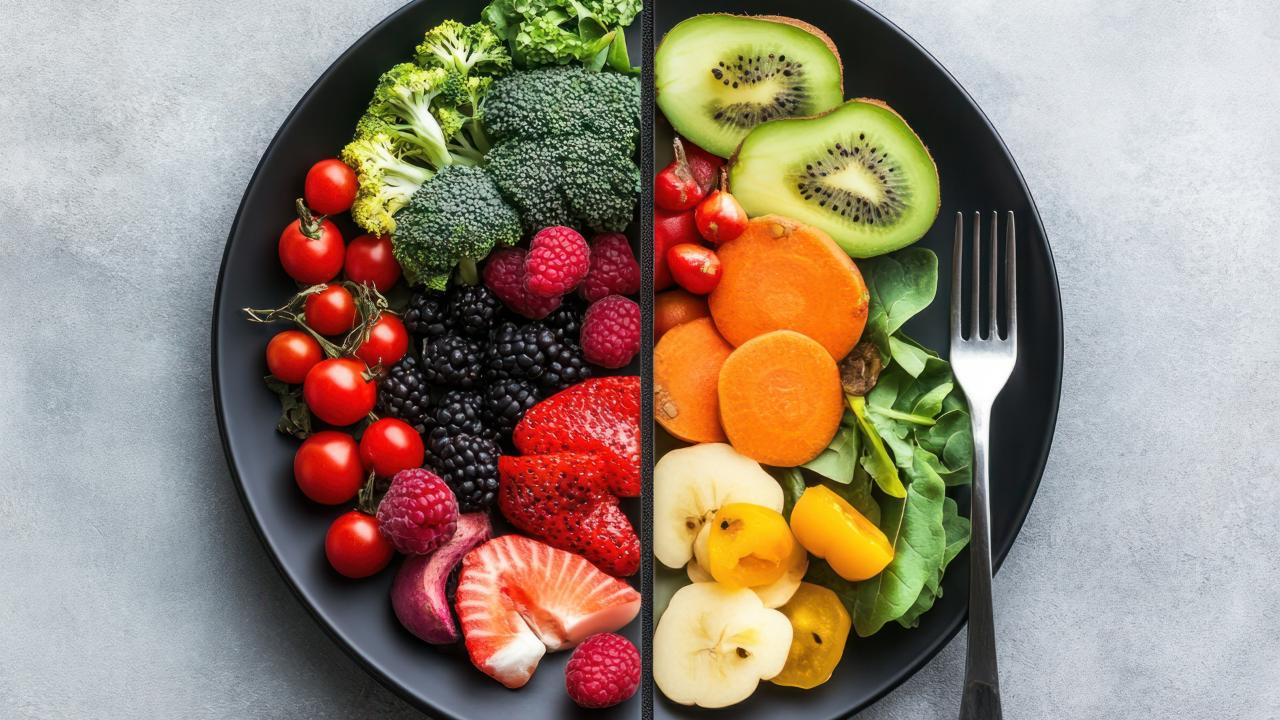

The consumption of western-style diet, with high intake of red and processed meat, low fiber intake, high fat and sugar intake, have been related to an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Obesity and physical inactivity are interrelated and could be a significant factor in the rising incidence among youth groups.
Gut microbiome disruption
Research points that alterations of the gut microbiome include reduced microbial diversity and the presence of certain pathogenic bacteria, and this is a major player in the etiology of colorectal cancer. Poor diet, overuse of antibiotics are all factors that may disrupt gut bacteria, increasing cancers
Genetic predisposition
Though early onset of CRC occurs without the identification of a genetic disorder, family history of CRC or syndromes inherited like lynch syndrome and familial adenomatous polyposis can significantly highly increase the risk of colorectal cancer. Patients with a first-degree relative with CRC younger than 50 years are a at greater risk afterwards.
Why early symptoms should not be ignored
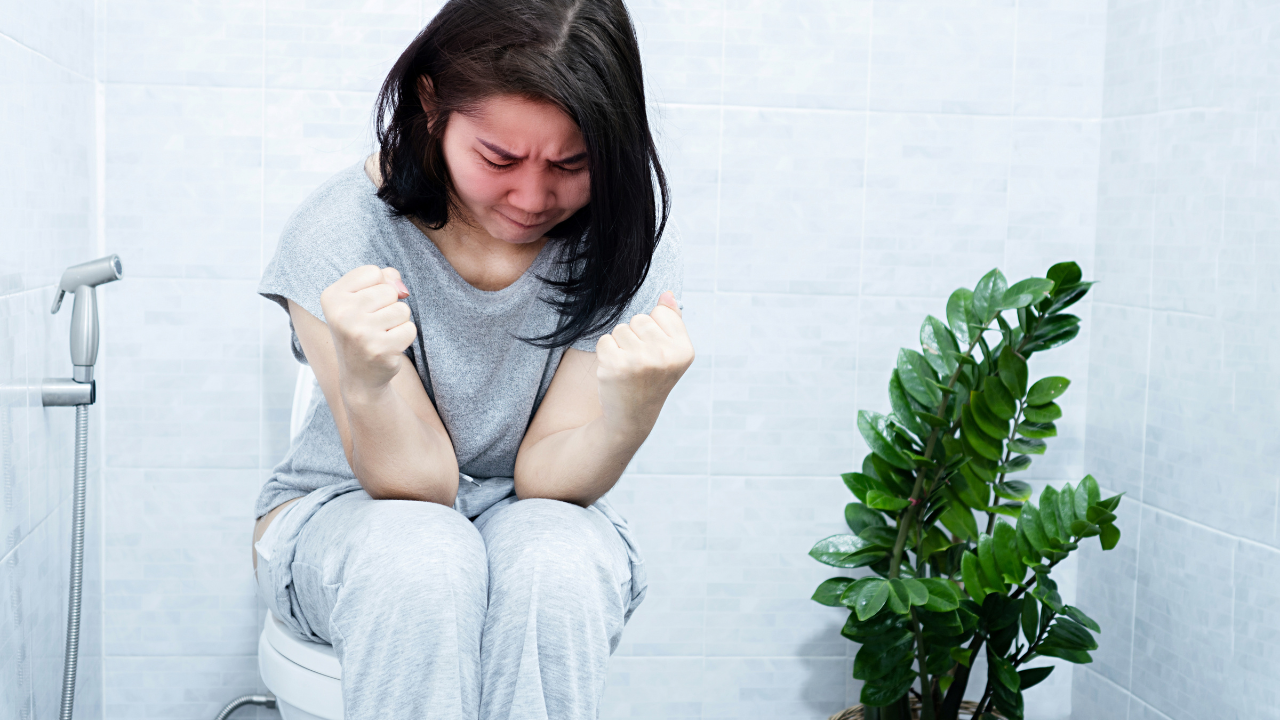

- Early recognition of symptoms of colorectal cancer can lead to earlier diagnosis and much more effective treatment:
- Changes in bowel movements, i.e., persistent diarrhea, or constipation, altered frequency or consistency of stool.
- Rectal bleeding or passing blood with bowel motion (bright or black-and-tarry blood)
- Unexplained prolonged fatigue associated with loss of weight, with no change in diet or exercise
- Persistent weakness and fatigue, potentially secondary to anemia due to bleeding within the body.
If any of these signs are lasting more than a few weeks, it is essential to see a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
Prevention strategies and strategies
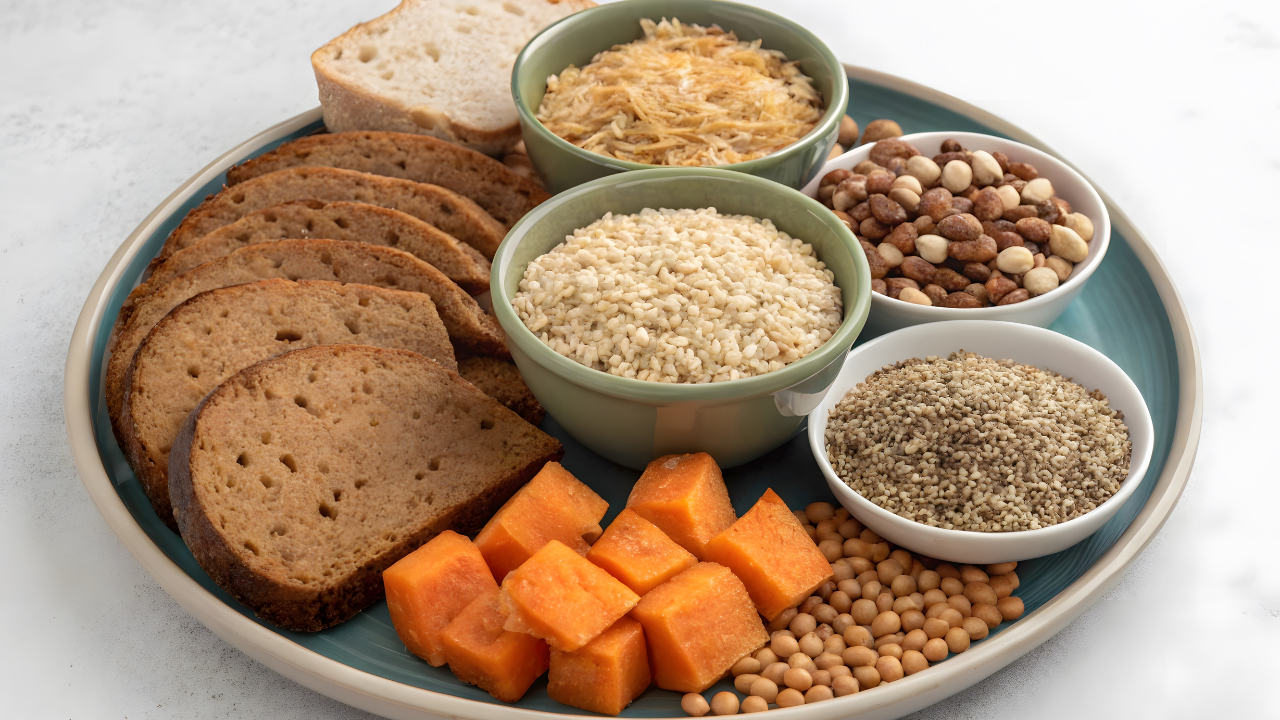

Changes in diet: Increase fruits, vegetables and whole grains, minimize red and processed meats, sugary and fatty foods as well.Screening and counseling: Individuals with a family history or known genetic tendency should be screened regularlyRestrict tobacco and alcohol use: Tobacco and alcohol use are the main risks for CRCEnhance gut health: Eating a healthy diet and probiotics to keep gut microbiome healthy, and restricting the use of excess antibiotics may decrease risk.Adequate physical activity: Exercise to maintain a healthy weight and overall wellness.What individuals do not comprehend is the fact that rising cases of colorectal cancer are a complex issue with lifestyle and genetic factors. With information and awareness regarding risk and early warning signs, individuals can actively approach prevention and early detection practices.